Updated FATF Standards for Virtual Assets and Virtual Asset Service Providers

Skeptics of cryptocurrency often cite concerns about crime as the reason they don't trust digital funds. Although it's true that cryptocurrency is not regulated in the same way as fiat currencies, there are strict standards in place that help prevent illicit activity. The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is the primary force behind many of these guidelines.
Established in 1989, the FATF has played a central role in combating money laundering and terrorist financing. Recommendation 15 (R.15) and the Interpretive Note to Recommendation 15 (INR.15) were developed in 2018 and 2019 to describe how Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASPs) should be regulated for anti-money laundering (AML) and countering the financing of terrorism (CFT) purposes. Since then, the FATF has closely monitored the implementation of these standards throughout the world. This article will explore the FATF's most recent findings and how they underscore the need for updated regulations, greater collaboration, and more consistent enforcement.
Insights from Recent Evaluation Reports
In their 2023 report, the Targeted Update on Implementation of the FATF Standards on Virtual Assets and Virtual Asset Service Providers, the FATF explains whether jurisdictions have enacted regulations, describes the challenges they're facing, and details why enforcement of R.15/INR.15 is so critical. The key findings from the report include:
- 75% of jurisdictions are not compliant or are only partially compliant with R.15/INR.15 requirements.
- More than 50% of jurisdictions have not taken any steps toward implementing the FATF crypto Travel Rule.
- Although the private sector has provided multiple tools to assist with FATF compliance, many of them do not meet the organization's standards.
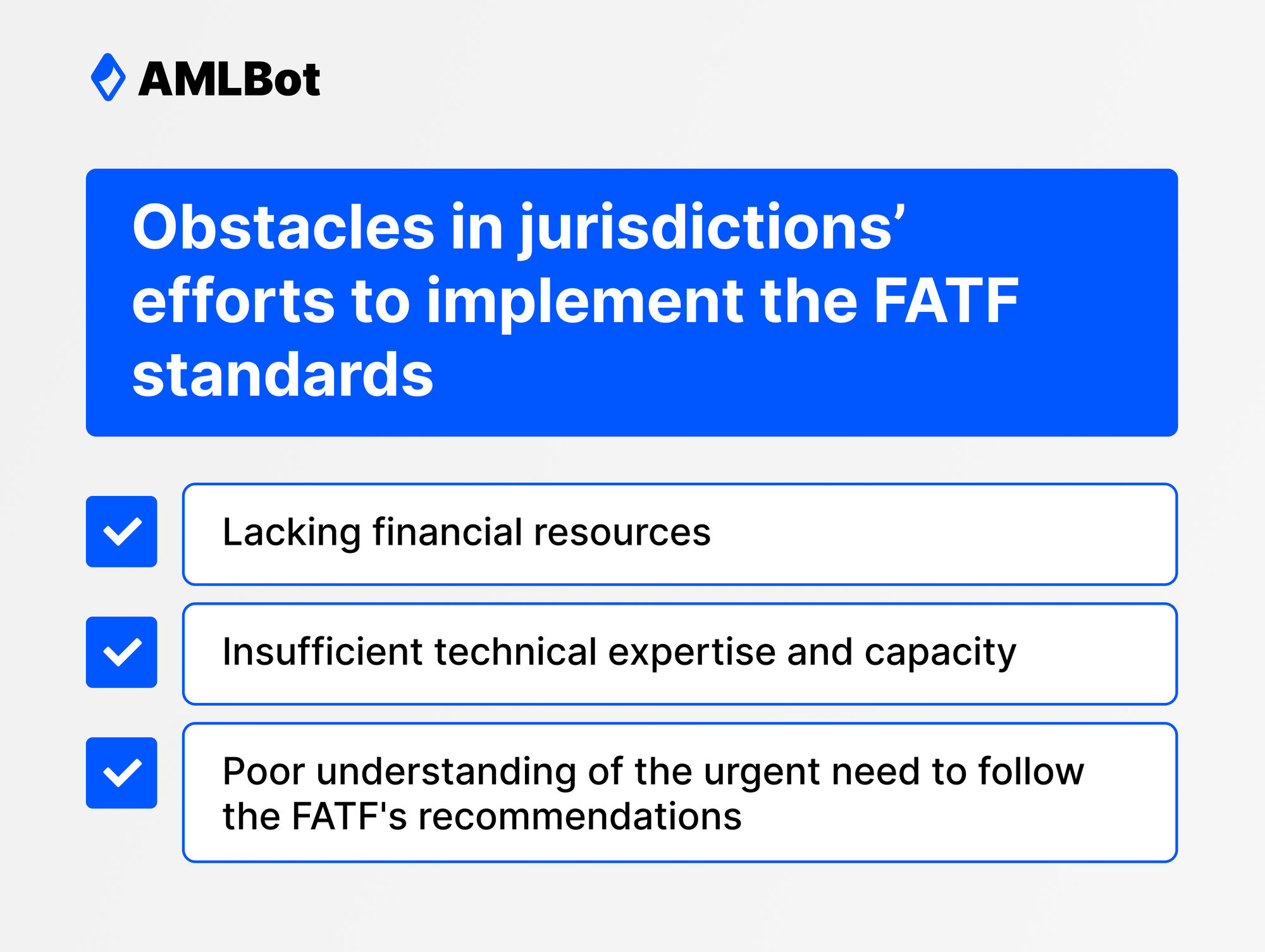
- Lacking financial resources
- Insufficient technical expertise and capacity
- Poor understanding of the urgent need to follow the FATF's recommendations
- Allowing jurisdictions to use the FATF's internal platforms to share training and presentation materials related to R.15
- Providing examples of regulations and legislation
- Offering guidance and assisting with risk assessments
- Sharing information about the implementation strategies of other jurisdictions
- Giving technical assistance
- Organizing sessions, forums, workshops, and webinars for training and collaboration
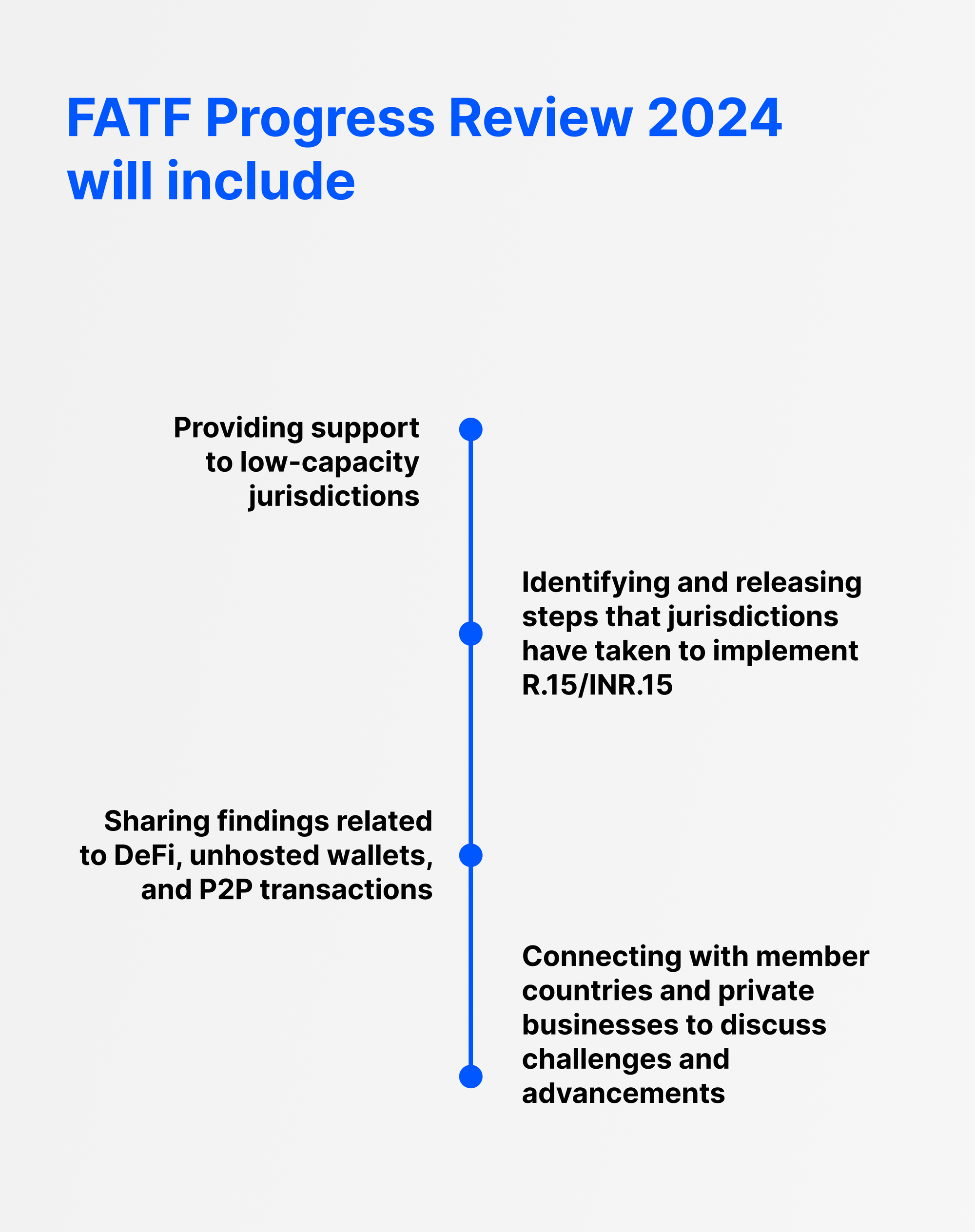
- Providing support to low-capacity jurisdictions
- Identifying and releasing steps that jurisdictions have taken to implement R.15/INR.15
- Sharing findings related to DeFi, unhosted wallets, and P2P transactions
- Connecting with member countries and private businesses to discuss challenges and advancements

Overall, the report paints a concerning picture of global compliance with FATF standards. Many jurisdictions have failed to follow through in meeting the FATF's requirements, placing crypto users and the industry as a whole at significant risk.
Implementation Hurdles
Although they may understand how the FATF regulates crypto, many jurisdictions have faced significant obstacles in their efforts to implement the standards. The vast majority have failed to conduct risk assessments and supervisory inspections, and regulations of the VASP sector remain lax.
Although some jurisdictions lag in complying with the standards because they aren't invested in reducing criminal activity related to digital assets, others have lagged in implementing the standards because of a common pattern of challenges, including:
Implementation of the FATF crypto Travel Rule has proven particularly problematic. The Travel Rule requires all crypto companies to include the personal information of a crypto user in any transaction above a certain threshold. This is critical because it makes it possible to identify suspicious users, reduce fraud, and prevent money laundering.
Unfortunately, because so many jurisdictions haven't implemented the Travel Rule, it's far less effective than it could be. During any crypto transaction, there's a high likelihood that at least one of the two companies involved is located in a jurisdiction where this screening process isn't required. As a result, the identification process for the transaction is incomplete.
Emerging Threats and Risks
Crime constitutes only a small portion of crypto transactions, but that can still translate to significant losses. The 2023 Crypto Crime Report from Chainalysis revealed that illicit addresses received a record-breaking $20.1 billion in cryptocurrency during 2022. Additionally, approximately 0.24% of all cryptocurrency activity was associated with illicit activity in 2022, a notable increase from the 0.12% share in 2021. This illicit activity takes a variety of forms.
Ransomware
Ransomware attacks are among the most concerning criminal acts related to cryptocurrency. According to the FATF's March 2023 Countering Ransomware Financing report, ransomware gangs almost exclusively use virtual assets during their attacks. Most gangs demand payment in Bitcoin, but they have also begun using anonymity-enhanced cryptocurrencies, also known as privacy coins, to make detection and tracing more difficult.
Sanctions Evasion
Concerns have also risen about the possibility of using cryptocurrency as a means of evading sanctions. In 2022, the United States Treasury Department released a statement describing suspected sanctions evasion by Russia, and North Korea has been known to use this practice for some time. Likewise, in May 2022, the Justice Department initiated a criminal prosecution of an American citizen accused of sending $10 million worth of Bitcoin to a virtual currency exchange in a sanctioned country.

Decentralized Finance and Unhosted Wallets
The FATF has emphasized concerns about decentralized finance (DeFi) and unhosted or peer-to-peer (P2P) crypto wallets. These types of crypto transactions generally present a higher risk of fraud and illicit activity. For instance, although DeFi remains a small portion of cryptocurrency transactions, it represented 82.1% of all stolen cryptocurrency in 2022.
Reducing crime related to DeFi and unhosted wallets is difficult because of the lack of oversight. Due to their structure, some DeFi arrangements fall under the category of VASPs and thus fall under the FATF's standards. However, jurisdictions sometimes struggle to determine which DeFi arrangements are subject to AML/CFT requirements. To help remedy this problem, the FATF plans to closely monitor this area of the market so that it can provide greater insight.
Global Assistance and Progress
One of the key aspects of the FATF's efforts to reduce criminal activity connected to cryptocurrency is supporting low-capacity jurisdictions. Specifically, the FATF has taken and will continue to take the following steps:
These steps, in conjunction with efforts made by the private sector, may help make jurisdictions more aware of the necessity of implementing the FATF's standards. The virtual asset landscape can only become more secure when there is widespread acceptance and understanding of AML/CFT measures.
Private Sector Dynamics
The private sector plays a vital role in improving Travel Rule implementation. Individual companies have developed a number of technological tools that assist VASPs as they attempt to comply. These tools are designed to help businesses in the crypto space mitigate risks and more closely adhere to the Travel Rule's requirements.
However, according to the FATF, many of these tools are not fully compliant with the Travel Rule. Thus, crypto companies using them may mistakenly believe that they're appropriately implementing the Travel Rule when in fact their approach is still lacking. Enhancing the technology designed to support Travel Rule compliance is essential for crypto companies around the globe.
For the private sector to truly contribute to the success of the Travel Rule, companies will have to work together to improve and modify their tools. The FATF indicates that it will continue to monitor the use of private sector tools, along with other trends, such as DeFi and P2P transactions.
Roadmap and Outlook
The FATF's February 2023 report references a roadmap that they will use to improve the rate of implementation for the Travel Rule and other crypto standards. The details of the roadmap have not been made publicly available, but the FATF has provided a general outline of its intentions for the near future.
The FATF plans to conduct a progress review by 2024. That review will include details from their upcoming activities, including:
While the FATF undertakes these and other attempts to improve Travel Rule implementation, all stakeholders, including crypto companies, private business leaders, and finance specialists, must collaborate to reduce the level of crypto fraud and illicit activity.
Understanding the Importance of FATF Standards
The realm of cryptocurrency is constantly changing in response to new technologies, public perceptions, and shifting regulations. While the FATF's Travel Rule and other elements of R.15/INR.15 have been controversial, they are intended to protect all participants in the crypto market from illegal activity and create a more stable landscape for virtual currencies.
The FATF's 2023 report may seem discouraging to crypto investors, companies, and regulators who are concerned about criminals exploiting digital assets. However, there are many reasons to believe that, with greater education, training, and support, jurisdictions will improve their approach to crypto regulations. If the public and private sectors come together to find solutions and share knowledge, the FATF's standards will become more ingrained in regulatory practices, creating a safer and more profitable space for everyone involved in the world of cryptocurrencies.