What Is KYC in Crypto? AML and KYC Explained

Summary
This article explores the role of Know Your Customer (KYC) as a foundational pillar of the cryptocurrency sector. It details how identity verification has transitioned from an optional practice to a mandatory legal requirement for regulated crypto businesses.
Definition and Purpose. KYC is the process of identifying and verifying a customer's identity before they access digital asset services. It serves to establish who a customer is and enable an informed risk assessment.
KYC vs. AML. While often used interchangeably, KYC is a specific process within the broader Anti-Money Laundering (AML) framework. AML sets the overall rules for preventing financial crime, while KYC provides the customer data needed to enforce those rules.
Core Requirements:. Crypto platforms (exchanges, custodial wallets, and brokers) must collect identifying information such as names, dates of birth, and government-issued IDs. Unlike traditional banking, this process is almost entirely digital and remote.
Ongoing Compliance: KYC is not a one-time event at onboarding. It involves continuous monitoring of transactions to identify suspicious behavior and compliance with the Travel Rule, which requires identity data to move alongside crypto transfers.
KYC is a structural necessity for lawful operation, protecting platforms from fraud, sanctions violations, and regulatory penalties while fostering long-term market growth. To streamline operations, crypto platforms frequently partner with specialized third-party KYC providers rather than building infrastructure in-house. These intermediaries offer automated, scalable solutions for document verification and biometric checks, reducing the technical burden on the crypto business.

KYC (Know Your Customer) in the crypto industry refers to the process of identifying a customer and verifying that customer’s identity before granting access to services involving a digital asset. In the cryptocurrency context, KYC requires a crypto platform, most commonly an exchange or custodial service provider, to collect identifying information such as name, date of birth, and government-issued documentation, and to confirm its authenticity. KYC is not a standalone obligation. It operates as a core component of AML (Anti-Money Laundering) frameworks designed to address Money Laundering, fraud, and other forms of financial crime.
KYC has become a mandatory requirement for most regulated crypto business activity. As cryptocurrencies evolved from experimental technology to widely used financial instruments, regulators concluded that crypto markets could not remain insulated from identity-based oversight. As a result, cryptocurrency exchanges, wallet providers, and other VASP (Virtual Asset Service Provider) entities are now expected to apply customer identification and due diligence measures comparable to those used in traditional financial services. These requirements reflect a broader regulatory objective: integrating crypto activity into the formal financial system while reducing systemic risk.
This article explains what KYC means specifically in the crypto sector, how it differs from and supports AML Obligations, and why it is legally required for most crypto platforms. It also outlines how the KYC process typically works in practice and why KYC plays a central role in crypto adoption.
What Does KYC Mean in Crypto
KYC (Know Your Customer) in crypto refers to the legal and compliance requirement for a crypto business to identify a customer and verify that customer’s identity before providing access to services involving a digital asset. In the cryptocurrency sector, KYC serves the same core purpose as in traditional financial services: establishing who the customer is and enabling an informed assessment of risk. However, KYC in crypto applies in a distinct operational and regulatory environment shaped by borderless access, remote relationships, and the pseudonymous design of blockchain-based systems.
In practice, crypto KYC differs from banking KYC in several important respects:
- Global Reach. Crypto platforms typically serve customers across multiple jurisdictions, rather than operating within a single domestic market.
- Remote Customer Relationships. Customer identification and verification are conducted without physical presence, relying on digital processes instead of in-branch interactions.
- Pseudonymous Transaction Layer. Blockchain transactions are recorded using addresses rather than names, making off-chain identity verification essential for compliance.
In the early development of the crypto market, many platforms operated with limited customer identification. As cryptocurrency activity became more closely integrated with the financial system, regulators determined that this approach posed comparable financial crime risks to those found in traditional finance. As a result, KYC expectations for crypto businesses were aligned with established regulatory standards. Today, KYC applies to a broad range of regulated crypto companies, including:
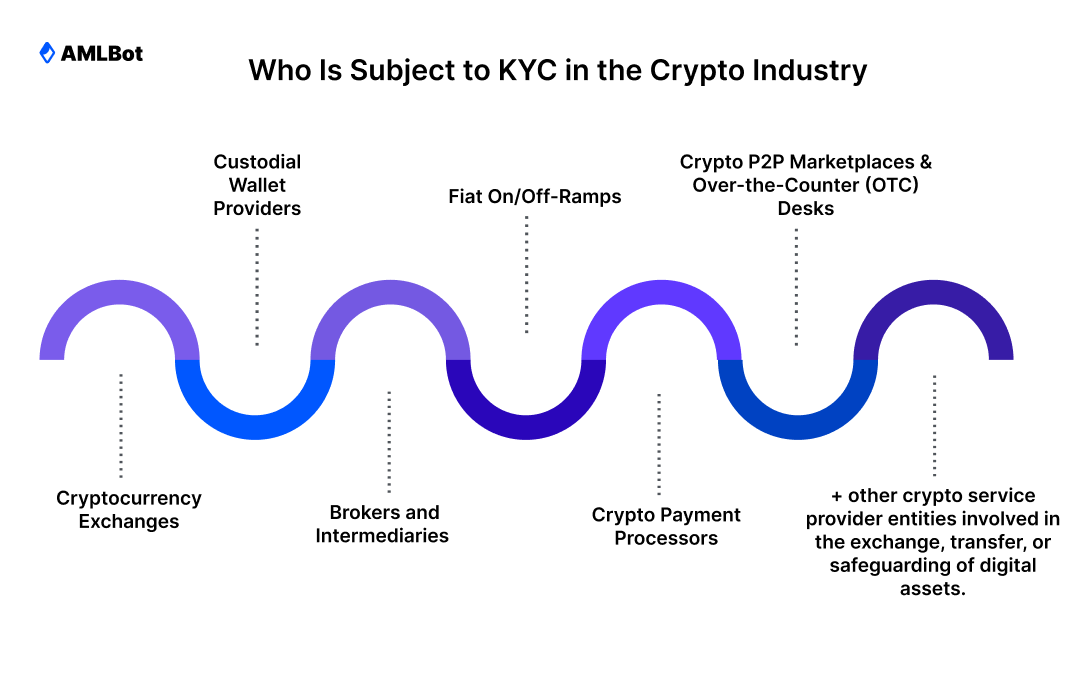
- cryptocurrency exchanges;
- custodial wallet providers;
- brokers and intermediaries;
- other crypto service provider entities involved in the exchange, transfer, or safeguarding of digital assets.
Under international standards issued by FATF (Financial Action Task Force), VASP (Virtual Asset Service Provider) entities are expected to apply customer identification and customer due diligence requirements similar to those imposed on traditional financial institutions, as outlined in FATF’s Guidance on Virtual Assets and Virtual Asset Service Providers. For any crypto business operating through a centralized legal entity, KYC is therefore not optional. It represents identity verification adapted to the crypto context and functions as a foundational element of compliance, risk assessment, and regulatory accountability across the crypto ecosystem.
What Is AML in Crypto and How It Relates to KYC
AML (Anti-Money Laundering) in crypto refers to the overall regulatory and compliance framework designed to prevent the use of cryptocurrency and other digital assets for money laundering, terrorist financing, and related financial crime.
In the crypto context, AML consists of Legal Obligations, Internal Controls, and oversight mechanisms that crypto businesses must implement to identify, assess, and mitigate financial risk. So, KYC (Know Your Customer) is one of the core components of this broader framework.
Beyond that, it is important to distinguish AML and KYC without separating them conceptually. AML defines the scope of obligations imposed on a crypto business, while KYC enables those obligations to be applied in practice. Rather than representing competing concepts, AML and KYC function in a structured relationship: AML establishes the compliance framework, and KYC provides the customer-level information necessary to enforce it. This distinction is central to understanding crypto regulation and compliance expectations.
AML vs KYC: Key Differences
The difference between AML and KYC lies primarily in scope and function. AML is a comprehensive framework that governs how a crypto business prevents and detects financial crime. It encompasses multiple processes, including internal governance, customer due diligence, risk assessment, transaction monitoring, record retention, and regulatory reporting. AML requirements are imposed through regulation and apply to the crypto business as a whole.
KYC, by contrast, is a specific process within AML. It focuses on customer identification and identity verification, enabling the crypto platform to establish the customer's identity and form an initial understanding of their risk profile. KYC does not replace AML obligations; instead, it supplies the factual foundation upon which AML controls operate.

Why KYC Is a Core Part of AML Programs
KYC is indispensable to AML compliance because several fundamental AML requirements cannot be fulfilled without reliable customer identification. AML frameworks are built on the assumption that a regulated entity knows who it is dealing with. Without that knowledge, core compliance obligations cannot operate as intended.
In particular, the following AML functions depend directly on KYC:
- Risk Assessment. Assessing customer risk requires verified identity information, including jurisdictional exposure, ownership or control structures, and the nature of the customer’s relationship with the crypto business. Without KYC, a crypto platform cannot reasonably classify customers as low-, medium-, or high-risk.
- Transaction Monitoring. Monitoring systems rely on KYC data to establish an expected behavioral baseline for each customer. Suspicious activity can only be identified by comparing actual transactions against a known customer profile. Where customer identity is unknown or unverified, transaction monitoring becomes ineffective.
- Regulatory Compliance and Reporting. AML regulations in most jurisdictions explicitly require customer identification and ongoing due diligence as conditions of lawful operation. Obligations such as suspicious activity reporting, sanctions screening, and compliance with the travel rule all depend on the ability to associate transactions with verified customer identities.
For crypto businesses, KYC is structural requirement. It enables AML controls to operate coherently and ensures regulatory obligations are applied consistently across customers, transactions, and jurisdictions. This is why KYC is universally recognized as a core pillar of AML programs in the crypto industry.
How KYC Works in the Crypto Industry
In the crypto industry, KYC (Know Your Customer) operates as a structured compliance process that begins before a customer gains access to services and continues throughout the customer relationship. Unlike traditional financial institutions, where customer onboarding often involves in-person interactions, crypto platforms typically conduct KYC through remote, digital channels. This reflects the global, online nature of cryptocurrency activity and the absence of physical boundaries in most crypto business models.
Although the mechanics differ from banking, the underlying objective remains the same: enabling the crypto business to identify the customer, assess risk, and meet ongoing AML (Anti-Money Laundering) and regulatory obligations. KYC in crypto, therefore, combines initial identity verification with continuous oversight to ensure compliance over time.
Identity Verification and Customer Onboarding
In the crypto, the KYC process begins at customer onboarding, when a customer seeks to establish a formal relationship with a crypto platform. At this stage, the platform must perform customer identification and identity verification sufficient to determine who the customer is and whether the proposed relationship presents an acceptable level of risk.
The scope of identity verification during onboarding typically differs depending on the type of customer:
- Individual Customers. Verification usually involves collecting basic identifying information, such as full name, date of birth, and residential address, and supporting it with government-issued identity documentation.
- Corporate Customers. KYC or (KYB, Know your Business) extends beyond the entity itself to include verification of the company’s legal existence, identification of beneficial owners and controllers, and the application of due diligence to those individuals.
These distinctions reflect the different risk profiles associated with natural persons and legal entities and are central to a risk-based compliance approach. Crypto onboarding is generally conducted remotely through digital channels rather than in-person interactions. This remote model allows crypto businesses to onboard customers across multiple jurisdictions while still complying with regulatory requirements. The depth and intensity of KYC applied during onboarding may vary based on factors such as customer type, requested services, and the outcome of an initial risk assessment.
Ongoing Monitoring and Compliance
KYC in crypto does not end once onboarding is complete. It functions as an ongoing compliance obligation that supports continuous monitoring of customer activity. Because customer risk can change over time, crypto businesses are expected to maintain up-to-date customer information and reassess risk as circumstances evolve.
Ongoing KYC enables transaction monitoring by providing the context needed to evaluate whether activity is consistent with a customer’s known profile. Changes in behavior, transaction patterns, or external risk factors may trigger additional due diligence or updates to customer records. In this way, KYC supports compliance not as a one-time check, but as a lifecycle process integrated into the broader AML framework.
The Role of the Travel Rule in Crypto KYC
The Travel Rule has reinforced the ongoing nature of KYC in the crypto industry. Originating in traditional finance and extended to crypto through international standards, the travel rule requires crypto service providers to transmit certain customer information alongside cryptocurrency transfers between regulated entities.
In practice, this means that when a transaction occurs between two regulated crypto platforms, both parties must be able to associate the transfer with verified customer identities. As a result, KYC is no longer limited to onboarding. It must remain current and accessible at the point of each qualifying transaction. The travel rule, therefore, links identity verification directly to the movement of crypto assets.
By requiring customer identification data to accompany transfers, the travel rule transforms KYC into a continuous compliance requirement rather than a static onboarding formality. It ensures that customer identity remains traceable across platforms and jurisdictions, closing gaps that previously allowed anonymous inter-platform transfers.
Why Crypto Platforms Are Required to Perform KYC
For most crypto platforms, operating without KYC (Know Your Customer) is not legally viable. As cryptocurrency activity became economically significant and increasingly interconnected with the traditional financial system, regulators concluded that crypto businesses must be subject to the same safeguards against financial crime as other regulated financial institutions. As a result, KYC is a legal requirement tied directly to the right to operate. Without KYC, a crypto platform cannot meet fundamental regulatory obligations, obtain or retain licenses, or maintain access to banking and payment infrastructure. In practice, this makes lawful operation impossible in regulated markets.
Regulatory Requirements for Crypto Businesses
Regulatory requirements are the primary reason crypto platforms must perform KYC. Across jurisdictions, laws and supervisory frameworks explicitly require crypto businesses to identify customers, apply customer due diligence, and assess risk as part of AML compliance. These obligations apply to cryptocurrency exchanges, custodial wallet providers, brokers, and other entities that qualify as VASP businesses and perform customer identification as part of regulated crypto activity.
In practice, KYC requirements for crypto businesses are enforced through several interrelated mechanisms:
- Statutory and Regulatory Obligations. National laws and regulatory rules require crypto businesses to perform customer identification, conduct ongoing due diligence, and monitor transactions for suspicious activity. For example, in the UK, the Financial Conduct Authority requires crypto-asset businesses to apply customer due diligence at the time of onboarding and to continuously monitor customer activity, as reflected in FCA guidance on crypto-asset AML compliance.
- Licensing and Registration Conditions. Crypto exchanges and service providers are typically required to demonstrate effective KYC and AML controls as a condition of authorization or registration. Supervisory authorities may conduct audits, request documentation, and impose corrective measures. Failure to comply can result in administrative penalties, license suspension or revocation, and legal liability for the business and its management.
- Access to the Financial System. Crypto platforms that lack adequate KYC controls generally cannot maintain relationships with banks, payment processors, or other financial counterparties. This practical constraint reinforces the reality that operating without KYC effectively excludes a crypto business from the regulated financial ecosystem.
Preventing Fraud and Financial Crime
Beyond regulatory compliance, KYC plays a central role in preventing fraud, money laundering, and sanctions violations in the crypto industry. By establishing verified customer identities, crypto platforms reduce the risk of anonymous misuse and create accountability for activity conducted through their services. In practical terms, KYC supports financial crime prevention in several key ways:
- Fraud Prevention. Verifying customer identity limits the ability to create false or multiple accounts, impersonate other users, or exploit crypto platforms anonymously. This reduces exposure to common forms of fraud and account abuse.
- Anti-Money Laundering Controls. KYC makes it more difficult for illicit actors to move, layer, or convert funds without detection. When customer identity is known, transaction monitoring, investigation, and reporting of suspicious activity become materially more effective.
- Sanctions Compliance. Screening verified customer information against sanctions lists allows crypto platforms to prevent restricted individuals or entities from accessing services. Without KYC, enforcing sanctions obligations in crypto environments would be largely impracticable.
Taken together, these functions explain why regulators view KYC as indispensable. It enables compliance with legal requirements, strengthens financial crime prevention, and underpins trust in regulated crypto platforms. For this reason, KYC is a structural condition for lawful and sustainable crypto business operations.
KYC and Crypto Adoption: Benefits and Challenges
KYC plays a dual role in the development of the crypto market. It supports the integration of crypto activity into the regulated financial system and contributes to trust and legitimacy, while also introducing operational and user-experience challenges that can affect adoption. This balance explains why KYC is often viewed as both necessary and controversial within the crypto industry.
Benefits for Crypto Adoption
When applied consistently, KYC contributes to several factors that support broader cryptocurrency adoption:
- Increased User Confidence. KYC reassures users that a crypto platform operates within a regulatory framework and applies controls designed to reduce fraud and illicit activity. This is particularly important for new users and institutional participants, for whom compliance is often a prerequisite for engagement.
- Access to Banking and Payment Services. Effective KYC enables crypto businesses to maintain relationships with banks, payment processors, and other financial counterparties. This access is essential for fiat on- and off-ramps and for integrating crypto services into the wider financial system.
- Regulatory Legitimacy and Market Scalability. Compliance with KYC requirements allows crypto platforms to obtain licenses and operate across multiple jurisdictions. Clear regulatory alignment reduces legal uncertainty and supports long-term market growth.
Challenges for Crypto Adoption
At the same time, KYC introduces constraints that can slow or complicate adoption:
- Impact on User Experience. Identity verification requirements can add friction during onboarding and reduce the immediacy that originally characterized cryptocurrency use, discouraging some users from participating.
- Compliance Burden for Crypto Businesses. Implementing and maintaining KYC processes requires ongoing investment in systems, personnel, and regulatory oversight. For smaller crypto businesses, these costs can be high.
- Tension with Privacy Expectations. KYC reduces anonymity and requires the collection of personal data, raising concerns among users who value privacy or fear data security risks.
In practice, KYC functions as both an enabler and a constraint. It supports trust, financial integration, and regulatory acceptance, while also introducing costs and friction that affect user behavior and business models. As crypto adoption continues to evolve, the industry's challenge lies in meeting KYC and AML obligations while minimizing unnecessary barriers to participation across crypto platforms.
How Crypto Businesses Typically Implement KYC
Because KYC obligations are complex and ongoing, crypto businesses typically approach implementation as a structured compliance function rather than a one-time technical task. The objective is not merely to collect customer information, but to integrate KYC into broader compliance, risk management, and operational frameworks.
At a high level, KYC implementation in a crypto business typically involves the following elements:
- Centralized KYC Governance. Crypto businesses define internal policies that determine when KYC is required, how customer risk is assessed, and how compliance decisions are documented. These policies are aligned with applicable regulations and licensing conditions.
- Outsourced Identity Verification with Internal Oversight. While identity verification is often handled by external service providers, responsibility for compliance remains with the crypto business. Internal compliance teams review outcomes, manage exceptions, and ensure that KYC decisions align with regulatory expectations.
- Risk-based Application of KYC Requirements. KYC processes are usually applied proportionately, based on customer type, activity, and risk level. This allows crypto platforms to differentiate between lower-risk and higher-risk relationships while maintaining consistency with regulatory requirements.
- Integration with Ongoing Compliance Controls. KYC implementation is designed to support ongoing monitoring, customer reviews, and regulatory reporting. Customer identification data is not treated as static but as part of a broader compliance lifecycle.
- Adaptation to Regulatory Change. As crypto regulation evolves, KYC frameworks are updated to reflect new requirements, supervisory guidance, and international standards. This ensures that KYC remains aligned with current legal expectations rather than becoming outdated.
In practice, this model allows crypto businesses to meet KYC obligations efficiently while maintaining operational focus on their core services. By combining external expertise with internal compliance oversight, crypto platforms can implement KYC in ways that support regulatory compliance, scalability, and long-term sustainability without turning KYC into a purely technical or ad hoc exercise.
KYC in Europe: What Crypto Businesses Should Know
KYC obligations for crypto businesses vary by jurisdiction, and Europe applies a particularly detailed and prescriptive regulatory framework. The European Union has taken an active role in extending AML (Anti-Money Laundering) rules to crypto activity, with legislation that not only reflects global standards but, in several areas, goes beyond them.
Crypto businesses operating in the European market or serving customers located in the EU must comply with a growing body of regulations, including the AMLR (Anti-Money Laundering Regulation) and related measures adopted as part of the EU’s AML package. These rules impose strict requirements on customer identification, prohibit anonymous crypto accounts, and reinforce ongoing compliance and monitoring obligations for regulated crypto platforms.
In Europe, crypto businesses must comply with specific AMLR and KYC requirements that go beyond general global standards. As European oversight continues to evolve, including the establishment of centralized supervisory authorities, crypto businesses should expect heightened regulatory scrutiny. Understanding the EU-specific approach to KYC is therefore essential for any crypto business seeking to operate lawfully and sustainably within the European market.
Conclusion
KYC (Know Your Customer) in crypto refers to the requirement for crypto businesses to identify customers, verify identity, and maintain ongoing oversight of customer activity involving digital assets. What began as a limited practice in the early days of the cryptocurrency market has become a standard obligation across regulated crypto platforms, reflecting the industry’s integration into the broader financial system.
KYC is mandatory because it is essential to AML (Anti-Money Laundering) compliance and is required under international standards and national regulations. Without KYC, crypto platforms cannot perform effective risk assessment, transaction monitoring, or sanctions screening, nor can they meet licensing and reporting requirements. As a result, operating without KYC is generally incompatible with lawful crypto business activity and exposes platforms to significant legal and financial risk.
In this context, KYC is not merely a procedural formality but a structural requirement that supports trust, security, and regulatory legitimacy in the crypto ecosystem. While it introduces compliance costs and user experience challenges, KYC remains a foundational element of sustainable crypto adoption.

-AMLBot Team
Connect with AMLBot:
🔗 Website
🔗 Telegram AML Bot
🔗 AMLBot Support Team
🔗 AMLBot LinkedIn
🔗 Our Blog
What Is KYC in Crypto, and Why Is It Important?
KYC (Know Your Customer) in crypto refers to the requirement for crypto businesses to identify customers and verify their identity before providing services involving digital assets. It is important because it enables compliance with AML (Anti-Money Laundering) laws, helps prevent fraud and financial crime, and allows crypto platforms to operate legally within regulated financial systems.
What Is the Difference Between KYC and AML in Cryptocurrency?
KYC is a specific process focused on customer identification and identity verification. AML is the broader compliance framework that includes KYC, risk assessment, transaction monitoring, reporting, and internal controls. In practice, KYC is a foundational element of AML.
Who Is Required to Comply With KYC Rules in the Crypto Industry?
KYC requirements apply to regulated crypto businesses, including cryptocurrency exchanges, custodial wallet providers, brokers, and other virtual asset service providers (VASPs). Any crypto platform that facilitates the exchange, transfer, or custody of digital assets through a centralized entity is typically subject to KYC obligations.
What Information Is Usually Collected During Crypto KYC?
Crypto KYC generally involves collecting basic identifying information such as name, date of birth, and address, supported by government-issued identity documents. Depending on the customer type and risk level, additional information may be required, particularly for corporate customers.
How Does KYC Work in Practice for Crypto Platforms?
In practice, KYC is conducted through a digital onboarding process in which customer information is collected, verified, and assessed for risk. Once onboarding is complete, KYC continues through ongoing monitoring and periodic updates to customer records.
Can Crypto Services Operate Without KYC?
In most regulated jurisdictions, crypto services cannot operate legally without KYC. While some decentralized protocols may function without customer identification, centralized crypto businesses are generally required to implement KYC to meet regulatory and licensing requirements.
How Does KYC Affect Privacy and Data Protection in Crypto?
KYC reduces anonymity by linking crypto activity to verified identities. As a result, crypto businesses are required to implement strong data protection measures and comply with privacy laws governing the storage, use, and retention of personal data.
What Risks Do Crypto Businesses Face if KYC Is Not Properly Implemented?
Failure to implement KYC can expose crypto businesses to regulatory penalties, license revocation, reputational damage, and increased risk of fraud and financial crime. In serious cases, non-compliance can lead to business shutdown or criminal liability.
How Often Should KYC Checks Be Updated in Crypto Compliance Programs?
KYC checks should be updated periodically and whenever customer risk changes. Regulatory frameworks generally require ongoing due diligence, meaning customer information must remain accurate and up to date throughout the relationship.
How Is KYC Handled Differently by Centralized and Decentralized Crypto Platforms?
Centralized crypto platforms typically apply full KYC as part of onboarding and ongoing compliance. Fully decentralized platforms generally do not conduct traditional KYC, although regulators continue to assess how compliance obligations should apply to decentralized models.