How Not to Become a Victim Of Fake Websites – AMLBot's Experience

The cryptocurrency industry is known to make it to the news cycles frequently because of negative happenings like hacks and attacks. As a result, several cryptocurrency users face situations where their funds get depleted from their wallets. Unfortunately, it is only in the aftermath of their loss that most realize how the funds, unbeknownst to them, were moved to wallets owned by shady entities. While there are measures that one can take to reduce the chances of such events from occurring, cybercriminals are always a step ahead, waiting for their next victim.
Presently, the cryptocurrency industry is plagued by cybercriminals who are using various methods to scam user funds. However, such cryptocurrency heists do not necessarily involve cybercriminals penetrating security measures or exploiting bugs in a platform's code.
Instead, they can attack users directly, who are sometimes the weakest link in the chain. They use techniques that deceive users, gain their trust, or combine both elements. They manipulate users into revealing confidential information like passwords and private keys through said measures.
At this point, the scammers deflect the funds from user wallets. If not, smart contract code designed to transfer away funds from web3 wallets is set as booby traps behind genuine links. In AMLBot's case, cybercriminals were found using multiple methods in succession to scam their clients.
It observed the presence of multiple fake websites, fake communication accounts, and social engineering attempts where scammers set up meetings pretending to be key figures in its operations. They even used on-chain smart contracts behind links on fake websites that facilitated the extraction of funds from its clients' web3 wallets.
The sour affairs with cybercriminals and the tactics they use to rob people of their cryptocurrency have motivated AMLBot to share its clients' and experiences with everyone.
Crypto Scams That AMLBot Detected

AMLBot and its clients encountered multiple attacks that the company eventually addressed and shot down. However, it realized that the scams were sophisticatedly designed to gain funds even from its wariest clients. They involved precise measures that allowed the scammers to trick clients using AMLBot's brand and resemblance. The scams most effectively executed by cybercriminals were phishing, social engineering, and contract confirmation scams. Let's look at how they work individually.
Phishing Scams
Cybercriminals use fake websites to scam people out of their funds. The misleading websites are usually identical to real ones operated by popular businesses in the cryptocurrency space and beyond.
Scammers can get fake websites to pop up at the top of search results or link them through emails or chats. Unsuspecting users click on them and end up on websites they believe to be the real deal. There, they give up their wallet details and allow scammers to gain control over their cryptocurrency. Similarly, fake applications are launched on application markets that users end up installing. The final result resembles that of fake website scams.
Social Engineering Scams
Phishing scams can be considered social engineering scams, but they extend beyond that. Social engineering scams include various others like baiting, tailgating, and others. They involve scammers impersonating important personnel from the companies like cryptocurrency exchanges and wallet manufacturers. The scammers can also assume bogus, non-existent identities that may seem important to victims.
They use the authority of their apparent identities to trick users into revealing confidential data like wallet private keys and account passwords. Once the needed information is acquired, scammers are quick to act on emptying as many funds as they can from users.
Otherwise, they use indirect methods that help steal user funds. For example, scammers convince users to download malware on their devices that snoop on their activity, allowing for collecting confidential data needed to pull out funds from their wallets.
Contract Confirmation Scams
The usage of smart contracts by cybercriminals to steal cryptocurrency is on the rise. Since most users do not look at the code that makes up their contracts, scammers can set them up to deplete user wallets without their knowledge. In addition, users believe that the contracts can execute certain functions while they move out all the funds from the wallets that users connect to them.
Such risky contracts are being placed behind links on fake websites and transfer user cryptocurrency to scammers during successful phishing exploits. Additionally, contract confirmation scams are the last step in elaborate crypto attacks, where phishing and social engineering scams lure victims to shady contracts.
AMLBot's Encounter with Crypto Scams
AMLBot faced the issue where cybercriminals used phishing, social engineering, and contract confirmation scams in unison. The attackers posed as the firm gained the confidence of their clients and other crypto users and managed to walk away with cryptocurrency belonging to those individuals. The cybercriminals organized attacks by creating websites that looked exactly like the AMLBot website. The domain name, too, was quite similar, with slight alterations that were deceptive enough to dupe the unmindful eye.
The scammers went far enough to create fake emails and communication accounts for all AMLBot staff. It allowed them to make the communication appear legitimate, thereby increasing trust, gathering sensitive information, and getting the clients to execute the scammers' wants. The social engineering scams got orchestrated so meticulously that one of the scammers managed to get an online meeting going on behalf of AMLBot's CEO with one of its most reliable clients.
The scammers succeeded in phishing attempts by getting clients to land on a copycat website linked during their communications. Further, they also targeted cryptocurrency users who wanted to switch their cryptocurrency for cash on cryptocurrency exchanges. The attackers asked the users to verify that their cryptocurrency did not come from risky sources. They pitched AMLBot's service for verification. However, they linked a fake website where the users lost their funds when they tried to verify them.
The fake website was quite like the original one, however, with a very slight deviation. amlbolt.com was one of the fake websites linked to clients, while the real website is amlbot.com. The deviations were often that subtle, therefore, tricking AMLBot's clients.
The prime difference between AMLBot's website and the copycat one was that the "check a wallet" button on the dashboard worked differently on both websites. On the real website, it allows clients to log in to their AMLBot accounts or create new ones. The fake website used the button to connect to a smart contract that could extract user cryptocurrency. By clicking the button on the fake website, the users technically allowed the smart contract to transfer out all the cryptocurrency stored in their wallets without their knowledge.
How AMLBot Defends Itself and Its Clients from These Issues
Although cybercriminals are getting smarter and managing to take users for a ride, AMLBot proactively takes action to prevent its clients from being victimized. In this scenario, it took multiple steps to address the fake websites that popped up in its likeness and went about scamming users.
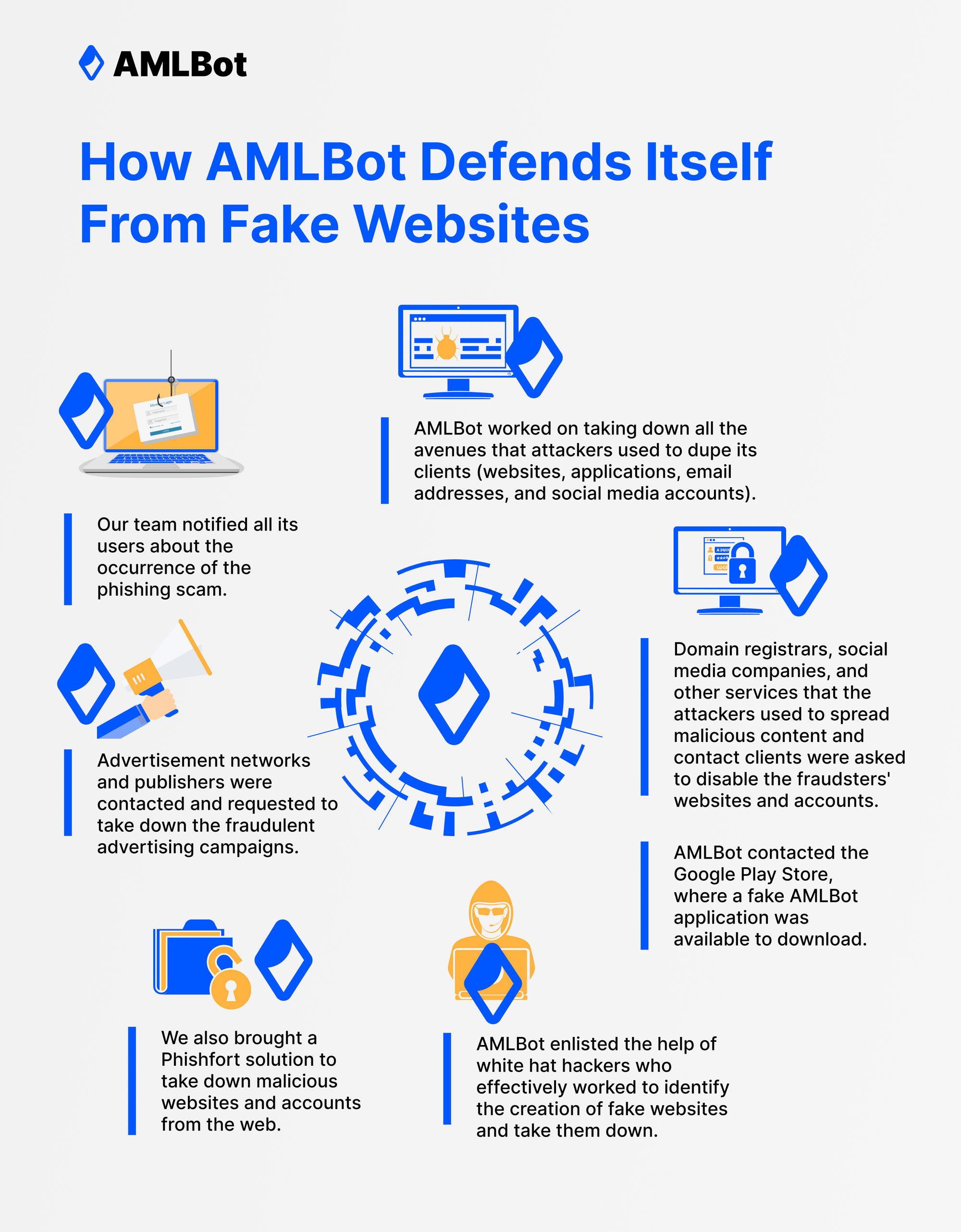
The first line of action was to notify all its users about the occurrence of the phishing scam. Its team communicated with every single client and provided them with information regarding fake websites, applications, and other lines of communication. The clients were also informed about identifying AMLBot's communication channels and website.
Simultaneously, AMLBot worked on taking down all the avenues that attackers used to dupe its clients. That included websites, applications, email addresses, and social media accounts. Domain registrars, social media companies, and other services that the attackers used to spread malicious content and contact clients were asked to disable the fraudsters' websites and accounts.
AMLBot even contacted the Google Play Store, where a fake AMLBot application was available to download. But, of course, installing the application on any device meant the users were at a severely high risk of losing their cryptocurrency.
Its team also noticed that advertisements on the internet drove traffic to sources like the fake application on the Google Play Store and myriad other fake websites. Advertisement networks and publishers were contacted after this discovery and were requested to take down the fraudulent advertising campaigns.
Beyond AMLBot's efforts, it also brought specialized solutions to avert these specific issues. Services like Phishfort exist to take down malicious websites and accounts from the web. Due to their vast network with several domain registrars, social media firms, and other internet-based businesses, they can effectively and quickly remove the operations of malicious actors from the web. To reach the parts of the web that AMLBot could not immediately, Phishfort and a few others got hired to do the job.
Similarly, AMLBot enlisted the help of white hat hackers who effectively worked to identify the creation of fake websites and take them down, preventing them from hurting AMLBot and its clients. AMLBot realized that the first line of defense in such situations is proactively taking immediate action against new threats as they emerge. White hat hackers can precisely do that and, ergo, defend AMLBot's interests against cybercriminals looking to grab a piece of the pie.
What Cryptocurrency Businesses Can Do When They Face Similar Issues

Because of increased phishing attacks throughout the industry, cryptocurrency businesses should take a page from AMLBot's book and stay vigilant of such occurrences. Any project can get impersonated, and resources should get dedicated to preventing or taking down such threats.
Constant Lookout for Fake Websites
Players in the industry need to keep an eye on emerging copycats. Emerging and popular businesses are at high risk of being impersonated by cybercriminals for their benefit. Thus, businesses must frequently scour the web for lookalikes and fakes claiming to be them. Not only do such instances trick users, they can also ruin the reputation of the businesses they are emulating.
Taking Down Phishing Attempts
When fakes get detected, businesses can request domain registrars and companies housing imposter accounts and applications to remove the fraudulent mechanisms. Also, they can hire phishing takedown services like AMLBot did to remove threats more efficiently off the web. Simultaneously, they can introduce phishing protection solutions into the workflow of their employees that constantly screen their devices for emails and messages containing malicious links.
Hiring Cybersecurity Experts
Furthermore, cryptocurrency projects and businesses need to enlist the services of white hat hackers and cybersecurity experts to know where their security is lacking. Besides looking for vulnerabilities within the projects' systems, white hat hackers and cybersecurity experts can look for phishing scams that leverage the reputation of real businesses and take them down. It is the precise reason why AMLBot enlists the help of such professionals.
Such measures are necessary for businesses to protect themselves and their reputation while simultaneously making it safer for their users. Alongside cryptocurrency businesses, users, too, should remain vigilant about phishing scams as their funds are usually on the line.
What Users Can Do to Prevent Getting Scammed by Phishing Attacks

Businesses and projects can take all the safety measures they want – some cybercriminals are always one step ahead. That is why the onus falls on the user to be wary as they use various cryptocurrency solutions.
Double-Checking Websites Before Transacting
Users need to be aware of the links they follow and the websites they land on. First, one should verify if the website they are on is legitimate, especially when funds are involved. It can be done by carefully examining the URL of the website the user is on.
They can verify it against resources on the company's social media and other resources. However, since the fake website epidemic is on the rise, one can never be too sure about the website they land on. Especially those that users will transact or provide sensitive information on.
Double-Checking Accounts Before Communicating
Heightened vigilance should also be maintained while communicating with accounts claiming to be from crypto businesses. Users should only respond to communication coming from legitimate sources. They need to verify the accounts that the messages get sent from. Email from fraudulent sources can often be identified by the domain name in the email address.
Likewise, fraudulent social media and instant messages come from fake accounts resembling real ones. A glance at the profile is always in order before responding. Also, it is a must to know what communication lines the company uses – messages from elsewhere should get ignored and the sender blocked. It is a best practice to block and report fraudulent accounts.
Disconnecting Web3 Wallets From dApps After Use
Awareness of the websites that users are on and the accounts they interact with is important to ward off phishing and social engineering scams. At the same time, they also need to pay heed to their web3 wallet connections to prevent contract confirmation scams.
Wallets should be connected to DeFi projects that are legitimate. Disconnecting the wallet from the project websites as soon as the transactions are done is important. Certain projects have gone rogue and continue to do so. Leaving wallets connected to projects for long periods can get risky.
Sometimes it takes effort to figure out all the websites to which the users' web3 wallets are connected. In such instances, services like Revoke can be used. Such services let users know all the dApps their web3 wallets are connected to and allow them to revoke the permissions they no longer intend to give. Some dApps can continue spending cryptocurrency from connected wallets. Revoke, and its counterparts can help prevent users from transacting the funds they do not want to.
Conclusion
Phishing attacks have always been a threat to web-based businesses and users. The threat gets enhanced with cryptocurrency due to its digital implementation. Therefore, cybercriminals are looking to pull a fast one over cryptocurrency users all the time.
Moreover, the novelty associated with cryptocurrency and the inexperience most users possesses while using it make it highly convenient for grifters to take what they can from users. Additionally, cryptocurrency being unretrievable once stolen makes it the perfect target for cybercriminals.
That explains the ever-increasing scams associated with cryptocurrency as the asset class' adoption continues to increase. Fake website phishing scams are highly prevalent in the cryptocurrency industry, as experienced by AMLBot. However, that should encourage users and projects to embrace cryptocurrency.
AMLBot's preventive actions can be observed by all cryptocurrency projects that look to protect themselves and their users from the looming threat of cybercriminals. Concurrently, cryptocurrency users must be aware of the websites and applications they access and always follow the best practices while handling their valuable crypto assets.