Automated KYC for Crypto: Best Practices to Reduce Fraud

Automated KYC is becoming a standard part of crypto compliance because it helps businesses verify who is onboarding— quickly and consistently. Instead of relying on purely manual review, automated KYC uses defined checks to support customer identity verification during customer onboarding, reducing friction while keeping controls in place where they matter most. If the concept of an automated KYC system is new to you, it can be hard to separate the buzzword from the actual process. In practice, automated KYC verification is a workflow: collecting identity data, validating it, and screening it against relevant risk signals before granting access to crypto services.
This guide explains how the automated KYC process works in a crypto context, why it matters for fraud prevention, and what best practices help you implement automated KYC checks without compromising usability or consistency.
Crypto Fraud and the Role of Automated KYC
Fraud remains a practical risk for crypto companies and users, especially at the point where new accounts are created and first transactions are enabled. Automated KYC helps address this risk by standardizing customer identity verification during customer onboarding, so identity checks do not depend solely on manual review or inconsistent internal routines.
In operational terms, automated KYC verification is a workflow: identity data is collected, validated, and screened before access is granted. Automated KYC checks reduce exposure to impersonation and synthetic identities by verifying documents and linking them to the applicant, and by running structured screening against relevant databases and watchlists. This is done before a customer conducts any cryptocurrency transactions, which helps limit downstream disputes, account abuse, and preventable fraud scenarios.
Combining blockchain and KYC technologies is central to that effort. KYC checks mitigate the risk of fraud by confirming each new customer's identity and rooting out any potential associations with criminal activity, such as money laundering. This occurs before a customer conducts any cryptocurrency transactions, helping reduce your business's liability and making it less likely that your customers will fall victim to fraud.
What Is Automated KYC in Crypto Compliance?
Automated KYC (Automated Know Your Customer) is a technology-driven identity verification process used to evaluate new applicants and support customer onboarding. It is not simply “KYC Online” or a digital form—automated KYC refers to a defined set of verification checks and decision logic that can be applied consistently, with reduced reliance on manual handling. In a crypto compliance context, automated KYC typically combines identity data capture, document and biometric verification, and screening checks into a single operational workflow that produces an onboarding decision and an audit trail.
Automated KYC in Cryptocurrency: Core Checks and Processes
A KYC automation process defines how identity data moves through checks, decisions, and audit logs within customer onboarding. The goal is not to replace accountability, but to make customer identity verification repeatable and scalable without turning onboarding into a slow, fully manual queue.
In traditional KYC systems, companies manually review a customer’s information, including identification documents, confirm that details are accurate, and check the applicant against watchlists or databases. They also assign employees to handle exceptions and follow-ups. This approach is time-consuming and prone to inconsistent outcomes, especially when onboarding volumes increase.
An automated KYC process shifts routine verification work into standardized checks, while reserving manual review for edge cases. In other words, the KYC automation system is designed to reduce unnecessary manual steps, not eliminate human oversight where judgment is required.
Automated KYC Checks Used by Crypto Platforms
Automated KYC checks are the operational controls applied to identity data to support an onboarding decision. In a crypto setting, these checks are generally aimed at answering three questions: Is the identity real? Is the applicant the rightful owner of that identity? Are there relevant risk signals that require additional review or restrictions?
Depending on the onboarding model, automated KYC checks commonly include:
- Document verification to assess whether identity documents appear authentic and internally consistent.
- Biometric or liveness verification to confirm that the applicant is a real person present during verification, and to reduce impersonation risk.
- Database and watchlist screening to detect risk signals that may require enhanced review or rejection under internal policy.
- Consistency checks across submitted data (for example, mismatched document fields, repeated reuse patterns, or anomalies that trigger manual escalation).
These checks are not “features” in a product sense—they are compliance and onboarding controls that support customer identity verification with consistent logic.
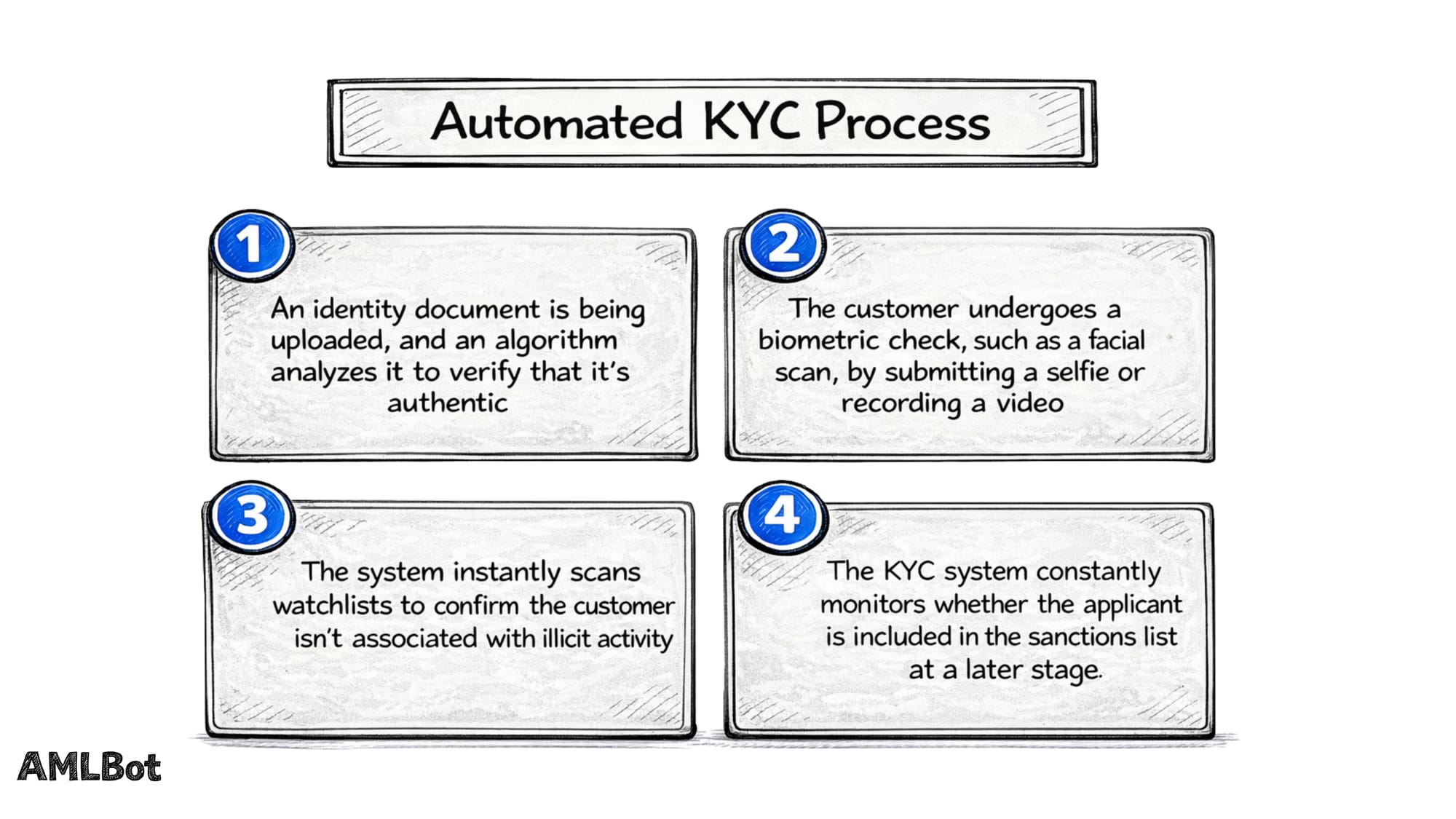
How the Automated KYC Process Works
At a high level, automated KYC verification follows a data-to-decision flow: identity data is collected, automated KYC checks are applied, and the system produces an outcome (approve, reject, or route to manual review). The intent is to keep routine decisions fast and consistent while ensuring exceptions are handled with appropriate scrutiny.
A typical automated KYC process includes:
- Data Capture During Customer Onboarding (Identity Details, Documents, and, where used, Biometric Inputs).
- Verification Checks (Document Authenticity, Liveness, and Data Consistency Controls).
- Screening Checks against relevant datasets used for risk assessment and compliance requirements.
- Decisioning and Audit Logging so the result can be justified, traced, and reviewed later if needed.
This structure is why automated KYC checks are closely tied to scalability: the same workflow can be applied across growing onboarding volumes without forcing a proportional increase in manual reviewers.
Best Practices in Implementing Automated KYC
Knowing how to implement a KYC automation process is primarily an operational task: defining checks, setting decision rules, and ensuring the workflow behaves predictably under real onboarding conditions. The strongest implementations are not the ones with the most complexity, but the ones with clear logic, clear exceptions, and clear accountability.
- (a) Define the Workflow Before You Automate It: document the automated KYC process end-to-end—what data is collected, what checks run, what triggers manual review, and what outcomes are allowed. This is how a KYC system supports compliance consistently in day-to-day onboarding.
- (b) Set Clear Exception Paths: automated decisioning should not pretend every case is identical. Define what “Cannot be Verified” means operationally (missing data, failed liveness, mismatched fields) and route those cases into a controlled manual review process.
- (c) Train Staff Around Escalation: team training should focus on reviewing exceptions, understanding audit logs, and applying consistent decisions—not on improvising steps that undermine the kyc automation system.
- (d) Validate Outcomes Through Periodic Review: don’t assume the workflow stays correct. Review false positives/negatives, escalation rates, and re-verification outcomes, and adjust verification rules where necessary.
- (e) Balance Controls with Usability by Measuring Friction: automated KYC verification should reduce unnecessary steps for low-risk users while preserving stricter verification where policy requires it. Track drop-off and escalation reasons so you can fix avoidable friction without weakening controls.
These steps help you integrate a KYC automation process into customer onboarding in a way that is stable, auditable, and scalable.
Automated KYC Verification Best Practices
Automated KYC verification works best when verification outcomes are explainable and consistent. That means the verification workflow should be designed so that each decision can be traced to a specific check, and each check has a defined purpose.
Practical Verification-Oriented best Practices Include:
- Use verification thresholds that can be justified, and keep them consistent across onboarding channels.
- Separate “Verification Failure” from “Risk Concern” (so that document or liveness issues do not get mixed up with screening-related escalation).
- Maintain an Audit Trail (that captures inputs, checks performed, decision logic, and reviewer actions (where manual review occurs).
- Control Manual Overrides (with clear permissions and logging, so exceptions do not silently become the default process).
This is the difference between “automation” as a label and automated KYC verification as an operational system.
Risk-Based Automation and Ongoing Monitoring
Risk-based Automation means the intensity of checks is calibrated to the risk profile of the applicant and the onboarding context. Not every customer onboarding case needs the same level of review, but higher-risk signals should trigger stricter verification, additional checks, or manual escalation.
Just as importantly, automated KYC is not always a one-time event. Identity verification supports ongoing risk controls by providing structured customer data that can be re-checked when circumstances change—for example, if a customer’s risk profile changes, if a re-verification event is triggered, or if updated screening datasets require re-screening.
In practice, the main value of ongoing monitoring is operational: it reduces gaps created by “verify once and forget,” while keeping the workflow manageable by focusing escalation where risk signals warrant it.
Case Studies: Success Stories of Automated KYC in Reducing Fraud
Automated KYC is easier to evaluate when you look at how organizations structure onboarding controls in practice. The examples below illustrate common approaches—standardized verification steps, documented escalation paths, and automation that reduces manual handling for routine cases while tightening review where needed.

Binance
For example, in November 2023, they agreed to pay more than $4 billion to resolve charges related AML Compliance Violations. Binance's current system has evolved far beyond the 2023 settlement. By 2025-2026, under the oversight of independent monitors, the exchange shifted to a 'Compliance-First' architecture. This includes the mandatory KYC for all sub-accounts (enforced since May 2024) and the integration of AI-driven behavioral monitoring to detect account sharing. Operationally, this reflects the transition to continuous risk assessment, where identity verification is just the first step in a perpetual monitoring loop required by the new EU AMLR standards.

Coinbase
As of 2026, Coinbase has evolved its 2019-era automation into a sophisticated AMLR-compliant ecosystem. Beyond standard ID and video verification, the exchange now operates under a full MiCA License, utilizing a unified KYC framework across the Eurozone. Operationally, Coinbase has moved from simple 'repeatable checks' to integrated traceability. Through its leadership in the TRUST Network, it ensures that identity data moves seamlessly with transactions, fulfilling the TFR (Travel Rule) mandates. Furthermore, its scoring mechanisms now trigger real-time risk reassessments based on blockchain behavior, effectively bridging the gap between static identity and continuous transaction monitoring.
Challenges and Considerations in Automated KYC
Implementing automated KYC is a systems and workflow decision. Most problems arise when verification checks are unclear, data does not flow reliably between systems, or the manual review path becomes the default because exceptions are not designed properly. There are a number of operational factors to consider, including:
- (a) Cost and Resourcing: automation still requires maintenance—verification rules, exception handling, and review capacity. If manual review rates stay high, the process will not scale efficiently.
- (b) Integration Complexity: customer Onboarding, Identity Verification, and Downstream Account Controls must share data reliably. Poor integration leads to duplicate checks, missing audit logs, or inconsistent decisions across channels.
- (c) Privacy and Data Security: automated workflows centralize sensitive identity data. Security controls, access management, retention policies, and audit logging become critical operational requirements.
- (d)Change Management: verification workflows evolve—datasets, thresholds, and escalation logic may change. Without disciplined versioning and testing, updates can produce inconsistent onboarding outcomes.
Integrating Automated KYC into AML Workflows
KYC is often a primary source of structured customer data used in broader financial crime controls. If automated KYC checks are poorly integrated, downstream controls may inherit incomplete identity profiles, inconsistent risk attributes, or missing audit trails, creating operational blind spots.
The key challenge is not “AML Regulation,” but data quality and workflow alignment: onboarding decisions, customer profiles, and risk flags must be consistent across systems. When integration is done well, identity verification results can be reused for escalation, re-verification events, and ongoing risk controls without repeating the entire onboarding process.
What's Next for Automated KYC
Automation will continue to evolve toward more consistent verification outcomes, better exception handling, and workflows that reduce unnecessary manual review.
The operational direction is clear: fewer fragmented steps, clearer audit trails, and better alignment between onboarding decisions and downstream risk controls.
Another likely direction is stronger reuse of verified identity data across customer lifecycle events—such as re-verification triggers, updated screening datasets, and policy changes—so that automated KYC supports ongoing compliance workflows without forcing repeated full onboarding checks.
Finally, scalability will remain a CORE driver. As onboarding volumes grow, organizations will prioritize KYC automation systems that keep decision logic consistent and keep manual review reserved for cases that truly require human judgment.
-AMLBot Team

Follow AMLBot:
🔗 Website
🔗 Telegram
🔗 Support Team
🔗 LinkedIn
Frequently Asked Questions About Automated KYC
Why is KYC Important in the Crypto Industry?
KYC supports customer identity verification and helps identify applicants whose onboarding should be restricted or escalated under internal risk policy. In a crypto context, this is critical for reducing avoidable fraud risk during customer onboarding and ensuring crypto compliance controls are applied consistently.
How does Automated KYC Differ from Traditional Methods?
Automated KYC relies on an automated KYC process—standardized verification checks, screening logic, and decisioning—so routine cases can be evaluated consistently with reduced manual handling. Traditional methods rely more heavily on employees to perform the same tasks manually, which typically slows onboarding and increases inconsistency across reviewers.
What Challenges does Automated KYC Solve?
Automated KYC verification improves throughput and consistency in customer onboarding by applying the same checks and decision logic across higher volumes. It also helps allocate manual review to the small percentage of cases that require judgment, which supports KYC automation + scalability.
How can Businesses Balance User Experience with Stringent KYC Processes?
The practical approach is risk-based: keep low-risk onboarding flows short and predictable, and reserve deeper verification for cases with risk signals or verification failures. Measuring drop-off, escalation reasons, and false positives helps reduce friction without weakening controls.
What are the Potential Risks of not Implementing KYC in Crypto Platforms?
Without a defined Identity Verification workflow, platforms increase exposure to impersonation, synthetic identities, account takeovers, and disputes. Inconsistent onboarding controls also make it harder to investigate incidents and justify decisions because audit trails are incomplete or missing.
How does Automated KYC Ensure Data Privacy?
Automated KYC can reduce unnecessary access to customer data by limiting the number of people who handle identity information and by centralizing audit logs. However, privacy depends on operational controls—access permissions, encryption, retention policies, and security monitoring—not on automation alone.
What Role does Regulatory Compliance Play in Automated KYC?
Automated KYC is commonly used to apply onboarding and identity verification controls consistently within a crypto compliance framework. The operational point is straightforward: documented checks, documented decision logic, and auditable outcomes are easier to maintain at scale than ad hoc manual handling.
Are There any Limitations to Automated KYC Systems?
Limitations typically come from workflow design and data quality: unclear escalation logic, high false positives, integration failures, or weak auditability. An automated system is only as effective as the checks it runs, the decision rules it applies, and the discipline used to review and improve outcomes over time.